
Dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs are known as osteochondrosis. This problem can occur in a person of any age. A dysfunction of the intervertebral discs leads to the development of many serious accompanying problems. How can the development of cervical osteochondrosis be prevented? What drugs and alternative therapies are used in treatment?
Cervical osteochondrosis - what is it?
The cervical spine consists of 7 vertebrae and 8 paired nerve nodes. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine develops into vitreous tissue against the background of the degeneration of the intervertebral pulp. In this case, pathological changes affect the ends of the nerve fibers and important vessels. Most often the pathology affects the 7th and 8th vertebrae.
The disease is carefully camouflaged as other pathologies, which are manifested in attacks of headache and discomfort in the neck. Patients may complain of dizziness, nausea, and pressure problems. Most often, the disease is confused with problems of the heart and blood vessels.
Important! Often, against the background of problems with the vertebrae, a person suddenly loses consciousness, feels a lack of air, and the tongue may become numb.
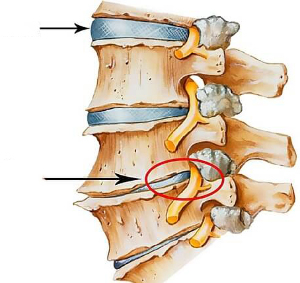
Cervical osteochondrosis is most often diagnosed in people over 30, which is caused by the peculiarities of the location of the human skeleton, constant statistical and dynamic loads. The disease is rapidly getting younger, recently osteochondrosis appears even in adolescents.
Causes of the disease
The development of osteochondrosis is influenced by physiological and pathological processes. They are closely related and in medical practice they are always considered together.
Physiological changes are caused by irreversible age-related processes in the cartilage of the spine. They are located in the central part of the intervertebral disc and are manifested by pinching of the pulp by fibrous tissue. Symptoms occur when the nerve endings are irritated.
Pathological changes - in this case the area of inflammation extends beyond the cartilage tissue and leads to severe irritation of the nerve endings and pinching of the blood vessels. They arise against the background of improper nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle that occurs in adolescents and middle-aged people.
Important! In rare cases, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine may go away on its own or manifest in the form of short-term episodes. The human body has many balancing and protective functions that can neutralize pathological changes in the cartilage for some time.
Triggering factors:

- sedentary work, lack of regular physical activity;
- frequent forced stay in an uncomfortable position;
- overweight;
- nervous overload, stressful states;
- neck and occiput injuries;
- hypothermia.
The cause of osteochondrosis can be congenital abnormalities and autoimmune diseases.
main functions
Cervical osteochondrosis does not always manifest itself in pain in a specific part of the spine. Often the disease has a blurred clinical picture.
The main symptoms are dizziness, migraines and sudden changes in blood pressure.
If an urgent hospitalization is required:
- numbness, loss of mobility in the muscles of the face or shoulder girdle;
- increasing headache associated with a deterioration in general well-being;
- lack of coordination;
- unconsciousness.
Pain in the cervical spine often radiates to the shoulder girdle and upper limbs. A distinctive feature is that the pain syndrome is paroxysmal, most often after waking up, making sudden movements, when laughing, coughing and sneezing.
If the osteochondrosis is in the initial stage, the pain subsides quickly, almost always accompanied by a crunch in the neck, the muscles become weak, the skin loses sensitivity.
Important! With pathological changes in the 6th vertebra, a pain syndrome can be observed in the thumb of the hand, with damage to the 7th vertebra affecting the middle finger.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women appear later than in men - the average age is 50–55 years.
How osteochondrosis is associated with other diseases
Cervical osteochondrosis and blood pressure - the link between these pathologies has long been established. With osteochondrosis, it is precisely the sharp drops in pressure during the day that are characteristic, persistent hypertension is not inherent in this disease.
Increased pressure in osteochondrosis is accompanied by migraines, head noises, pain in arms, legs and chest. At the same time, the sensitivity of the skin in the collar area is noticeably reduced, stress can cause a surge in pressure, a long stay in an uncomfortable position.
Cervical osteochondrosis and dizziness - occurs against the background of severe pain syndrome, impaired brain circulation and the transmission of nerve signals, as well as problems with the vestibular apparatus.
With osteochondrosis, non-systemic dizziness is most often manifested - there is no feeling of rotating objects, but the person is very sick, it is difficult for him to stay upright.
Important! With frequent attacks of dizziness, it is necessary to consult not only a neuropathologist, but also an ENT doctor to exclude the presence of pathological changes in the nasopharynx.
Headaches are associated with osteochondrosis in almost 90% of cases. It occurs against the background of vascular spasms, pinching of nerve endings and increased intracranial pressure. It manifests itself in different ways - pulsating, boring.
Headache attacks in osteochondrosis are similar to sensations in high blood pressure, angina pectoris, heart attack and stroke.

Panic attacks occur in osteochondrosis against the background of cerebral circulatory disorders. At the same time, a person experiences unreasonable fear, physical discomfort. The duration of the attack is 2-3 minutes to an hour, it can be repeated several times a day. Panic attacks are accompanied by a heavy head, incessant tears, apathy, and lethargy. In severe seizures, it is necessary to take sedatives and see a psychiatrist regularly.
With osteochondrosis, fears and depression arise against the background of constant pain, a forced change in the usual way of life.
Diagnostic methods
People with osteochondrosis may experience pain in the back of the head, chest, and arms. Such a blurred picture of the disease makes the initial diagnosis much more difficult.
Prevents timely diagnosis and uncontrolled use of painkillers by people. A person feels healthy without pain. He seeks medical help late, when irreversible processes develop in the tissues of the neck joints.
Important! Only one neurologist deals with the treatment of osteochondrosis.
An external examination reveals mobility and pain in the neck. After that, the doctor prescribes X-rays in multiple projections and computed tomography. Magnetic resonance imaging should be performed if an inguinal hernia is suspected. Doppler ultrasound is done to assess the condition of the arteries and blood vessels.
Principles of drug treatment
Drug treatment is aimed at eliminating pain, inflammation, restoring normal mobility and blood circulation.
Main drug groups:
- Analgesics in the form of tablets and injections are intended to eliminate the pain syndrome;
- nonsteroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Chondroprotectors help restore cartilage tissue;
- muscle relaxants relax the muscles, are used as an aid to pain relief - they contain glycerin, benzimidazole, have a large list of contraindications;
- vitamin complexes - must contain all vitamins of groups B, D, E, retinol, ascorbic acid;
- artificial analogues of histamine - help get rid of problems with the vestibular apparatus;
- means for external use in the form of gels, ointments - helps improve blood circulation, relieve cramps and pain, warm, relieve pain.
Important! Vitamins found in food are not enough to treat osteochondrosis.
Drugs that improve cerebral blood flow in cervical osteochondrosis are a mandatory part of therapy. They widen blood vessels and improve blood flow. Nootropics that improve metabolic processes in the brain, restore memory and thinking.
Surgery for osteochondrosis is rarely performed. An operation is essential if there are signs of paralysis of the upper extremities, an acute disturbance of the blood supply and cerebral edema.
Additional treatments include massage, manual push-and-pull therapy, metered traction, relaxation techniques, and acupuncture.
Treatment of osteochondrosis at home
At-home treatment includes the regular performance of special exercises and the use of special orthopedic devices. You can use traditional medicine recipes as supportive therapy.
The Shants collar was developed to relieve tension in the spine, reduce stress and strengthen the neck muscles. The head and neck are fixed in the correct position, which allows you to get rid of insomnia and prevent the progression of pathological changes. You don't need to wear a collar all day, but 2-3 hours before bed.

Self-massage helps relieve pain and cramps, while rubbed in ointments that improve blood circulation. The procedure should be carried out while sitting, the posture is comfortable, relaxed. It is necessary to stroke and rub in a circular motion to touch not only the neck, but also the shoulder girdle.
Important! With cervical osteochondrosis, any type of heating is prohibited, with the exception of a bath and sauna.
Medicinal baths relieve pain and inflammation well and allow the spine to relax. Water procedures should be done every other day, the course consists of 15-20 procedures.
Bath recipes:
- Mix 150 g of chamomile and mint, the mixture brews 5 liters of boiling water. Leave the infusion for 2 hours, filter.
- Take 20 g each of mint, lemon balm and birch leaves. The collection is brewed in 6 liters of boiling water after 2 hours of filtration.
- To prepare a sage infusion, you need 300 g of herbs and 5 liters of boiling water. The healing solution is ready in 2 hours.
For oral administration, you can prepare a yarrow infusion - this will help quickly get rid of inflammation, cramps and pain. 230 ml of boiling water brew 6 g of grass, leave in a closed container for an hour. Take 15 ml 3 times a day.
A solution of 15 g of sea salt and 1 liter of water helps treat osteochondrosis. Bring the mixture to a boil, let cool completely. In the composition, moisten natural fabric, apply to the neck.
Possible complications
With timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, cervical osteochondrosis proceeds without any particular complications. Otherwise, severe pathological changes will develop that can lead to disability.
Why is cervical osteochondrosis dangerous?
- vertebral artery syndrome - functional and organic changes caused by impaired blood flow to the brain;
- high blood pressure, arrhythmia;
- numbness, weakness, muscular atrophy of the upper limbs;
- protrusion, hernia;
- VSD;
- neurological disorders.
Physiotherapy exercises for osteochondrosis
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can restore nutrition in damaged tissues and restore blood circulation.
During therapeutic gymnastics, it is forbidden to turn your head sharply and make sharp bends. Only imitation of such movements is allowed. You cannot do a series of exercises for more than 2 minutes - prolonged exposure can lead to a complication of osteochondrosis.
Shishonin has developed a number of effective exercises to treat cervical osteochondrosis. The principle is that all movements must be performed smoothly, each position must be fixed for 15-30 seconds. There should be no painful sensations during gymnastics, each exercise should be repeated 5 times.
Description of the exercises:
- Sit up straight and tilt your head to the right. If muscle tension occurs, correct the position. Make 5 slopes on each side.
- Bending the head forwards and backwards is done analogously to the previous exercise.
- Extend your chin alternately to your left and right shoulder. The back is straight, you cannot round it off.
- Turns your head left and right in each position to linger for 30 seconds.
- Keep doing side turns, but using extra arms. When you turn to the right, your right hand should be on your left shoulder and vice versa.
- Close your palms, raise your arms above your head, and turn to your sides.
- Extend your arms, take them to the side and slightly back, straighten your chin forward.
Preventive measures
Prevention of osteochondrosis consists of simple steps. With regular use, serious health problems can be avoided. Prevention is especially important for the elderly and those who spend a lot of time sitting.
How to prevent osteochondrosis:

- shower hot for at least 10 minutes every day;
- visit the bathhouse and sauna regularly to relieve cramps and tightness in the neck.
- sleep on an orthopedic pillow and a special mattress;
- Perform a small five-minute warm-up every hour while sitting.
The best sports to prevent osteochondrosis are swimming, yoga, aerobic exercise and special gymnastics to strengthen the neck muscles.
People at risk are prohibited from running, jumping or bodybuilding. The critical weight is 10 kg, weights should be carried on two hands. In addition, you can use a corset that protects the spine.
Sergei Bubnovsky describes the preventive measures against osteochondrosis well. In his book you can find out which back pains are dangerous, how to restore health without injections and corsets, and find a number of special exercises.
Cervical osteochondrosis is a disease that can affect anyone. Timely diagnosis and prevention, as well as a healthy and active lifestyle, will help avoid the development of serious pathological changes in the spine, and will ensure good health and excellent mood.

















































