Everything you need to know about osteoarthritis - their causes, signs, varieties and diagnostic methods - helps to recognize the disease in the early stages. With effective treatment methods you can get rid of this disease. Arthrosis is characteristic of people over 40 years. In the past few decades, impartial statistics show that a tendency to rejuvenate men and women between the ages of 30 and 35.
What is osteoarthritis?
Arthrosis is a chronic joint disease, accompanied by pathological changes in the hyaline cartilage and then in adjacent tissues, a joint capsule and a synovial bowl. The defeat is dystrophic and degenerative nature, which leads to a change in the structure of joint tissues and the loss of its functionality. According to the data of the same statistics, osteoarthritis is subject to 12% of the total population of the planet. From 62% to 65% of all disease episodes, people over 60 years fall. Another 30-35% of the cases of joint damage to this pathology are in patients between the ages of 40 and 60. And about 3% are young people between the ages of 20 and 40.
The risk of joint disease is shown by the fact that it is practically not completely healed. However, when diagnosing the pathology in the early phase of the progression, it helps to maintain the functionality of the joint.
In most cases, cases of arthroselseions are diagnosed in such joints:
- Carpal compounds;
- Cervical and lumbar spine;
- Knee joint;
- Hip joint;
- Shoulder joint;
- Ankle;
- Metatarsophhalangeal joint.
The disease is more characteristic for the female population - representatives of the female half of the population suffer more often from this pathology at an older age. The osteoarthritis of the interfalance joint occurs ten times more often in women than in the male population.
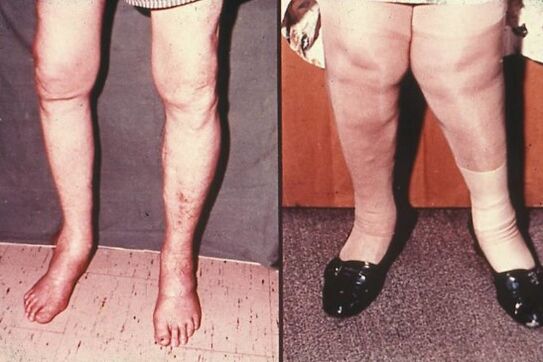
The likely consequences of osteoarthritis
In timely treatment, the disease manifests itself through less development intensity and consequently a stop of degenerative and dystrophic changes. This means that you enable timely surgical or therapeutic intervention to maintain the functionality of common, normal passage and to eliminate pain.
At the same time, the tightening causes frequent and stable pain, lameness and swelling of the joint. Progressive pathological changes in the tissue deprive the joint of its usual functionality. In a short time, arthrosis quickly flows into a chronic form in the absence of competent treatment. Such consequences lead to the need for constant medical observation and regular treatment of the disease during exacerbation times.
In order to avoid the consequences and complications with the first suspicion of its development, you should contact medical specialists. In the early phases of the progress of the treatment of the arthrosis of the joints, a rheumatologist is involved in the treatment. In chronic form, the treatment of this pathology is carried out by an orthopedic traumatologist.
Types of osteoarthritis
This pathology of the joints has different forms and varieties that differ in such criteria:
- Causes (primary and secondary form);
- Arthrosis stadiums (three progression stadiums are classified);
- Localization of the pathology (location of the disease and type of joint);
- Localization form (generalized and local form);
- The course of the disease (acute or chronic).
At the point of manifestation of symptoms, hips, knees, cizstics, elbows, shoulder, ankle and cervix arthrosis are distinguished.
According to etiological signs, pathologies of primary nature are classified, which develop without conditions and a secondary illness. In the latter case, damage to the joint occurs due to the development of infectious diseases in neighboring tissues, mechanical disorders, the loss of the physiological functionality of the joint and the consequence of a progressive inflammatory process, a hypothermia, an injury or other factors.
The classification in the form of localization includes local and generalized damage to joints. In the first case, the disease and its symptoms cover a small part of the joint or its individual tissue and components. With a generalized form, several joints are affected or one of them with complete coverage of all joint fabrics.
A different degree of intensity manifests itself in different stages of the progression of the disease. At the same time, symptoms and complications can be expressed brighter, more or less dynamically the process of destruction and impairment of the joint functionality.
Depending on osteoarthritis, they differentiate:
- Acute form;
- chronic form.
The acute form is usually shown by an increased intensity of the development of symptoms and its severity. Painful sensations appear stronger and morphological changes in the tissues are more dynamic. In chronic form, the course of the disease is slow, it manifests itself through separate signs in periods of tightening and practically does not heal.
Illness
During the disease, medicine distinguishes three stadiums, the differences in the signs of the disease, the intensity of damage and localization. At the same time, the distinction in all three stages relates to the types of fabrics that suffer pathological changes.
- The first degree of development of the arthrosis of the joints is the initial phase of the disease. It is characterized by a slight lesion of cartilage tissue and the loss of physiological functions in collagen fibers. At the same time, minor morphological diseases of the bone tissue and structural changes in the synovial fluid are found in the first stage. The cartilage of the joint is covered with cracks, the patient has a slight pain instead of the localization of the pathology.
- The second degree is the development of osteoarthritis with an increase in dynamics. This stage is characterized by the occurrence of stable pain, chroma. Remarkable morphological and dystrophic cartilage cartridges are found that bone growth showed during the diagnosis. Osteophytes are formed - bone growth that are visible during a visual examination of the destruction point. At the same time, the processes of degenerative changes occur in the synovial capsule, which leads to its structural exhaustion. The disease in this phase can often worse and be regular. The pain gradually becomes constant.
- The third degree is an active progression. Due to its degeneration, the synovial fluid is almost complete and bone tissue around each other. The joint mobility is almost completely missing, the pain becomes more tangible. Cartilage tissue also lacks degenerative and atrophic changes. The treatment of the third arthrosis degree of joints is considered impractical.
In addition to these three degrees of development in pathology, there is a final phase - irrevocable destruction of all common tissue. In this phase, it is not only impossible to carry out productive therapy, but also to remove pain syndrome.
The inflammatory process usually begins with a second degree of damage in rare cases in the absence of medical interventions in the first stage. Afterwards it becomes more difficult to stop it, and this can lead to secondary pathologies, the development of a pathogenic microflora is developing instead of the localization of the disease.
In order to rule out serious consequences, the treatment from the first degree and the use of intensive care methods should begin. In the last stage associated with the complete destruction of cartilage tissue, only a methodology for riding the patient from pain and the immobility of the joint is permitted - endoprosthetics with complete or partial replacement of the components of the joint.
Causes of the disease
The reasons can be primary and secondary factors. In older people, the disease can occur in mixed etiology, i. e. in the presence of primary and secondary causes. Their complex manifestation tightens the course of osteoarthritis and reduces the dynamics of recovery.
The main cause of most types of this pathology is a violation of the metabolism. Changed metabolic processes lead to morphological anomalies in cartilage and synovial fluid. As a result, the changes relate to the entire joint and are often accompanied by the origin of inflammatory local herds.
In addition to metabolic pathologies, the causes of the arthrosis of the joints are:
- Traumatic damage to individual tissue or overall connection. This includes transfers, fractures, ligaments, meniscus fracture and penetrating wounds. This reason is more common in people who are involved in sport or their activities are related to dangerous working conditions and physical exertion.
- An inflammatory process is often a factor as a secondary reason. In patients who suffer from gout, psoriasis, rheumatic anomalies and autoimmunpathologies, inflammation usually develop. The joints of the joint are subject to patients in the stage of exacerbation of infectious diseases, including tuberculosis, chlamydia, staphylococci and other contagious diseases;
- The consequences of the tightened form of respiratory diseases - flu, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory infections;
- Increased body weight of the patient - with a disproportionate strain on the joints of his tissue, constant mechanical effects suffer, which leads to morphological deviations and the destruction of the structure of the cartilage;
- Excessive hypothermia, which leads to the destruction of the integrity of the cartilage tissue and the loss of the structure of the synovial fluid;
- Thyroid diseases.
A separate place in the etiology of osteoarthritis is a genetic factor. It is the genetic anomaly that is able to disturb dysplasia of common tissues and the disturbance of the physiological functions of collagen fibers, which are responsible for the flexibility and mobility of the joint.
At the same time, other accompanying factors are the reasons for the development of this pathology: vitamin deficiency, intoxication based on products in views and excessive medicines, the advanced age of the patient, the pathological processes of blood formation and blood flow, hormonal abnormalities and diseases of the reproductive system of infectious origin.
The mechanism of progression of the disease
If one of the causes that provoke the disease of the joint with osteoarthritis occurs, pathological processes begin to develop. The mechanism of its progress is not completely investigated, but the main stages of official medicine are known.
In the initial phase, the structure of the cartilage tissue and abnormal changes in the synovial fluid occurs. All of this is due to violations of metabolic processes, in which common tissue does not receive the necessary components in sufficient quantities or withdrawn by some of them.
Next, the elasticity of collagen fibers and the flexibility of the cartilage is lost, since there is no time to produce hyaluronic acid in the body, which delivers the softness and flexibility of the structural composition of the collagen fiber. The cartilage gradually dries, becomes brittle and crack. The liquid in the synovial capsule is gradually exhausted and then completely disappears.
Fixed bone -noplasms are formed on the cartilage tissue. At the same time, the deformation of other articular tissue, its pathological degeneration, dystrophy and the loss of physiological activity is developing.
For the patient, these changes mean the occurrence of pain, lameness and immobility of the joint.
Symptoms of arthrosis
Signs of osteoarthritis of the joints occur from the first degree, although sometimes they are not so pronounced. Characteristic phenomena for all stages of osteoarthritis are:

- Pain syndrome;
- Crispy noises when moving;
- Inactivity or complete decrease in joint mobility;
- Swelling;
- Conformation of the joint.
pain
Pain usually occurs during movement. With intensive physical exertion, painful sensations increase a persistent trend. In all types of osteoarthritis, every place of its localization, the pain is sharp.
In the initial phase, the pain is weakened weakly, more often daily. Usually the pain is at short notice and refuses in peace. In chronic form and with intensive progression of the acute pain form, pain syndrome manifests itself more often, has an increased manifestation phase, which often bothers itself at night.

















































